

Fetogenesis: the fetus matures and grows.The proximal bones of the lower limbs start to ossify.
INFERIOR PHARYNGEAL CONSTRICTOR USMLE SKIN
Fingers are initially separated from one another by skin flaps, followed by complete separation. Organogenesis is complete by the end of week 8. The proximal bones of the upper limbs start to ossify. Formation of a physiological umbilical hernia. Eye is clearly recognizable through retinal pigment development. Auricular hillock development, which later becomes the auricle. Development and differentiation of additional pharyngeal arches. The mesonephros, which is formed between weeks 3 and 5, bulges in the urogenital ridge. Rapid head growth through development of the brain and facial structures. Weeks 5–8 of embryogenesis mainly involves organogenesis. Embryopathies: complex anomalies of individual organs during a time when the developing embryo is particularly susceptible to injury. Primitive circulation with a tubular heart and initial intraembryonic blood vessels. First heartbeat at week 4 of embryonic development (visible on transvaginal ultrasound). Development of upper and lower limb buds. Branchial apparatus → pharyngeal arches, pharyngeal pouches, pharyngeal grooves. Neurulation : ectoderm → neural plate → neural tube with neural pores, neural crest (closes by the end of week 4). Notogenesis: axial mesoderm → notochord → induces development of neural plate from ectoderm. Gastrulation: Epiblast cells → primitive streak → trilaminar disc ( endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm). Hypoblast → yolk sac, lining of chorionic cavity. The bilaminar embryonic disc develops ( 2 layers): epiblast and hypoblast. The maternal circulation becomes connected with the placental circulation. Syncytiotrophoblast begins secreting hCG (detectable in blood and urine one week and two weeks after conception, respectively). Trophoblast further divides into the syncytiotrophoblast, which is involved in the development of the placenta, and the cytotrophoblast, which forms the chorionic cavity, that surrounds the embryoblast. This may result in brief implantation bleeding: bloody vaginal discharge occurring during implantation (may be mistaken for menstruation). The trophoblast penetrates the endometrium. Implantation (embryology) of the blastocyst (most commonly into the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus). Multiple pregnancies: conjoined twins especially. Occurrence: up to 14 days after conception. Congenital anomalies: complex congenital anomalies with double malformations or missing body parts. 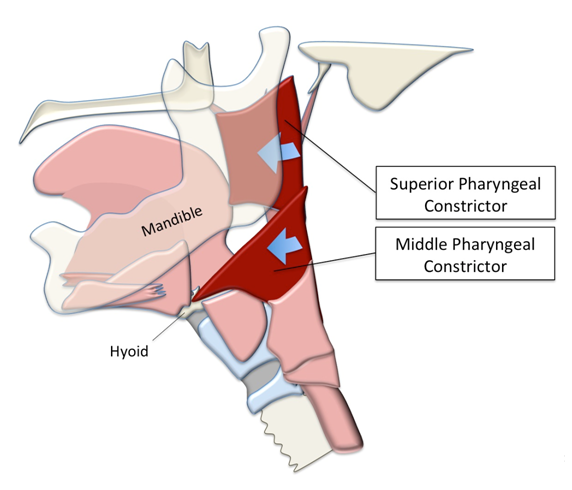
The blastocyst consists of 2 layers of cells: the outer trophoblasts and the inner embryoblasts.Division of the zygote into the morula ( 16-cell mass) and then the blastocyst.The zygote travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus.Chromosomal aberrations (e.g., trisomy).Conjugation (conception): fusion of the sperm and ovum to form the zygote (single cell).Consists of 2 phases: the acrosome reaction (dissolution of the spermatic cell membrane and the zona pellucida of the ovum) and impregnation (penetration of the sperm into the ovum).Fertilization ( conception): usually occurs in the fallopian tubes (most commonly in the ampulla) within 1 day of ovulation.Capacitation: maturation of the sperm in the female genital tract.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
